Procedural Level Generation for Augmented Reality Games
Abstract
Mixed reality games are those in which virtual graphical assets are overlaid on the physical world. We explore the use of procedural content generation to enhance the gameplay experience in a prototype mixed reality game. Procedural content generation is used to design levels that make use of the affordances in the player’s physical environment. Levels are tailored to gameplay difficulty and to affect how the player moves their physical body in the real world.
We argue that mixed reality games benefit from artificial intelligence beyond machine vision surface detection. In particular, we argue that a class of artificial intelligence algorithms called Procedural Content Generation (PCG) can automatically optimize players’ gameplay experience by accounting for the specific configuration of players’ unique physical environments. Procedural content generation is the use of algorithms to automate the production of various aspects of computer games, such as terrain, levels, missions, weapons, and monsters. Artificial intelligence approaches to PCG treat the creation of game content as an optimization problem —- the attempt to find a set of parameters for a specific type of content that maximizes an evaluation function.
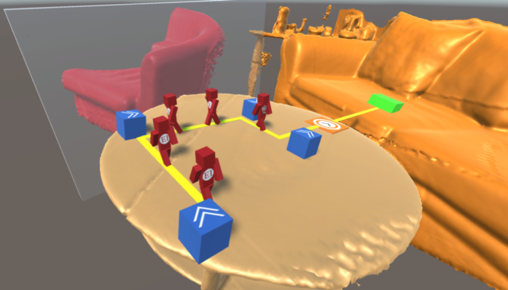
We introduce a mixed reality game, MR Lemmings, which uses PCG algorithms to place a set of virtual game assets that will affect the player’s interaction with the physical environment. The game was developed as a prototype for the exploration of the ways in which procedural content generation can reason about the affordances of physical environments in mixed reality games.